So many different revenue models…
But, which one fits your business?
Over the past few decades, many new revenue models have proven to be profitable.
That’s why I’m going to show you 16 different revenue models so you can evaluate if there might be a better way to monetize the value you deliver to your customer.
Let’s start…
What is a revenue model?
A revenue model is a company’s strategy for making money from the value it provides to customers.
A company often starts with an idea of how they can provide value to their customers…
In exchange for that value, the company makes money, but how exactly are you going to make that money?
A revenue model helps determine how to convert the value your customer receives into money the customer gives to you, this could be by taking out a subscription, agreeing on a one-time transaction or perhaps getting an hourly wage.
The revenue model is part of a company’s entire business model…
But, what revenue models are there?
I’ll show you:
16 different revenue models
I managed to find 16 different revenue models and what the advantages and disadvantages are…
Now it’s your turn to choose the best one:
1. Hourly wage
In an hourly wage-earning model, you sell time…
You predetermine an amount of money you want to earn per hour and for every hour worked you receive that same amount.
See: Hourly wage
Advantages
- It is tremendously simple and easy to structure.
- The value the customer receives is close to the value of the price.
Disadvantages
- It is not very scalable, there are only a limited number of hours in a day and as an agency, it is often a long process to hire many people.
Example
Think of a self-employed individual who gets paid by the hour for the work he delivers or an agency that sells its employees’ hours to third parties.
2. Transaction Model
In the transaction model, there is a one-time transaction…
Together with the buying party, the seller agrees on a price for which a certain product is sold.
See: Transaction model
Advantages
- It can be scalable in many cases.
- The value the customer receives is close to the value of the product.
Disadvantages
- Good thought needs to be given to complaint handling.
Example
When you buy stuff from a webshop or in a supermarket you make a one-time transaction in exchange for certain goods.
3. Subscription model
Instead of paying a certain amount each period, you can also choose to pay automatically every period.
The subscription model is often used in situations where there are a lot of repeat purchases or returning customers.
See: Subscription model
Benefits
- It is highly scalable.
- The subscription model provides good insight into expected revenue.
Disadvantages
- The value the customer receives may be high one period and low the next, but the customer pays the same amount in both periods.
Example
If you want to join a gym you sign up for a subscription so you can go as many times as you want each week.
4. Advertising model
If you manage to get people’s attention you can use that stage very well to sell sponsored space.
This can be in the form of ads or promotions…
See: Advertising model
Benefits
- Online it can be VERY scalable, but offline that is often not the case.
Disadvantages
- People generally hate ads and it is often difficult to determine how many promotions you can do before people lose interest.
Example
Facebook sells space on its online channel for ads, but also think of Max Verstappen participating in advertising campaigns for Jumbo.
5. Freemium Model
In the Freemium model, the product is initially free, but eventually, the user must pay to use the full product or functionality.
See: Freemium model
Advantages
- A free product usually generates a lot of publicity and users.
- Often the freemium model is highly scalable and everything can be measured properly to provide insight into effectiveness and revenue.
Disadvantages
- You make expenses for users who ultimately do not become your customers.
- If your freemium product is too good, users may choose not to purchase the full version.
Example
Spotify offers a free version of their app where you can listen to music, but you are regularly harassed with ads and you don’t have the option to download music.
If you decide to purchase the subscription you will be able to download music and you will no longer be bothered by ads.
6. Service model
First, you sell a product with a relatively low margin, on which you earn little…
Then you earn money on the periodic maintenance that must be done, which in the end still yields a fairly high-profit margin.
It may be that the customer constantly has to buy products or services from you, this is also called “vendor lock-in“.
Benefits
- A continuous stream of revenue and a clear understanding of the revenue you can expect.
Disadvantages
- Relatively low margin on the first sale.
- Customers may become dissatisfied, as it is difficult to get rid of you and they lose control.
Example
Suppose you buy a very cheap car from a garage but have to keep coming back for maintenance.
7. Bait Model
Similar to the service model, but with the bait model you first sell a cheap product and then let customers buy expensive parts…
The bait model is also called bait and hook or the Gillette model.
Profit is made on the extra parts the customer has to buy or the extra products the customer has to keep buying.
Again, vendor lock-in can occur.
See: Bait model
Benefits
- Easily scalable and the expected turnover is easy to understand.
- The customer is stuck with your company.
Disadvantages
- Customers may become dissatisfied, as it is difficult to get rid of you and they will lose control.
Example
Gillette sends young men who have just turned 18 a razor whereby Gillette incurs expenses at the first moment…
Then the young man has to keep buying Gillette razors every time which are relatively expensive.
8. License Model
You invent something once and you make money on it again and again…
If you invent something you can grant licenses, for example, copyright or patents.
By granting a license to someone you permit them to use your idea for a certain purpose.
See: License model
Benefits
- Very scalable, you only have to do something once.
Disadvantages
- What you made or what you have invented may not be relevant anymore within a certain period and then people will not buy licenses anymore.
Example
If a photographer takes a picture he can ask for money if other people use his picture to put on their website.
9. Rental model
You use certain goods very rarely so it is often not worthwhile to buy them…
In that case, some people own these goods and who, for a certain price, want to rent them to you for a certain period.
See: Rental model
Benefits
- It is tremendously simple, partly because the demand often already comes from the customer.
Disadvantages
- Maintenance is required on the goods that are rented out.
Example
If you are renovating your garden it can be very useful to rent a small excavator for a day.
10. Consumption Model
The customer pays for what it consumes…
See: Consumption model
Advantages
- Can be very scalable if you don’t get extra work if the customer starts using more resources.
- The value the customer gets is very close to the value the customer pays for.
Disadvantages
- Requires reliable measurability.
Example
With gas and electric companies, you pay for the amount you consume.
11. Brokerage Model
Receive a commission for the added value you offer between two parties
If you ensure a successful deal between two parties you can receive money for that, often in the form of a commission.
This model is also called the mediation model, affiliate model, or commission model.
See: Brokerage model
Benefits
- Can be very scalable if it is in the form of an online platform.
Disadvantages
- Often takes time to build a network in an offline situation and in the case of a platform it is difficult to build supply and demand simultaneously.
Example
PayPal receives a commission for every successful transaction that goes through its platform.
12. Production Model
You produce something on behalf of another party and get money for it…
Advantages
- You don’t have to be too busy keeping an eye on market changes, because customers come to you with what they want.
Disadvantages
- It is very important to align the expectations of your customer with what you can deliver.
Example
As a metal company, you may be commissioned by another metal company to deliver a certain quantity of a product.
13. Bundle Model
You sell a certain product and in doing so you immediately sell a related product…
The customer often cannot easily buy a particular product on its own, so it is often sold in combination with another product.
See: Bundle model
Benefits
- If the customer buys one product there is a very high chance that the customer will also buy the related product at the same time.
Disadvantages
- It may not be legally allowed.
Example
When you book a vacation you can buy travel insurance immediately.
14. Personalization Model
You create something customized for the customer…
Thus you create a product that specifically addresses the needs of one customer.
Benefits
- It’s easy to differentiate.
Disadvantages
- It’s not very easy to make it scalable.
Example
Think of a Nike shoe that can be personalized or a customer putting together their own Shampoo.
15. Donation Model
People donate money to you…
You are completely dependent on the goodwill people have because they are free to give how much they want.
Benefits
- People will never complain about the price. 😉
- It’s scalable.
Disadvantages
- It’s pretty impossible to maximize your revenue based on donations.
- You are very likely to have little room to invest.
Example
Wikipedia and Telegram are built entirely around user donations.
16. Arbitrage Model
You profit from the price difference between two markets supplying the same goods…
In other words, you buy a product in one market or on one platform and sell it at a higher price in another market or on another platform.
Advantages
- Very scalable.
Disadvantages
- It’s usually a matter of time before the arbitrage is gone.
Example
You buy a product at a cheap price on AliExpress from China and sell it on Amazon in other countries.
17. Blitzscaling
Favor rapid growth over efficiency and profit optimization.
You are going to invest a lot in the beginning to achieve the first-scaler advantage and get a bigger share of the market.
Advantages
- Helps amass a large market share.
- Extreme long-term profitability.
Disadvantages
- Huge cost at the beginning
Example
Amazon making relatively high losses at the beginning, but as retailers and consumers become dependent, it is much better able to set its own prices.
18. Brand Value
Invest in a well-known and reliable brand so that the financial value is ultimately stored in the brand.
A good brand allows you to charge higher prices which will eventually make it more profitable.
Benefits
- Less price-conscious customers
- Higher profit margin
Disadvantages
- Long process to build a well-known and reliable name
Example
Apple can charge a premium price for its products because of the strong brand they have built.
19. Cost leadership
Finding a lower cost structure to increase margins and offering products at the lowest possible price.
This works extremely well in markets with near perfect competition where price is one of the only aspects customers base their choice on.
Advantages
- If successful, you can convert high volumes extremely quickly.
Disadvantages
- It is a race-to-the-bottom in which you can only be successful if you are the cheapest option.
Example
Aldi puts boxed products on its shelves to save labor costs and therefore offer lower prices.
How do you choose a revenue model?
There are two types of revenue models…
- Symmetric Revenue Model:
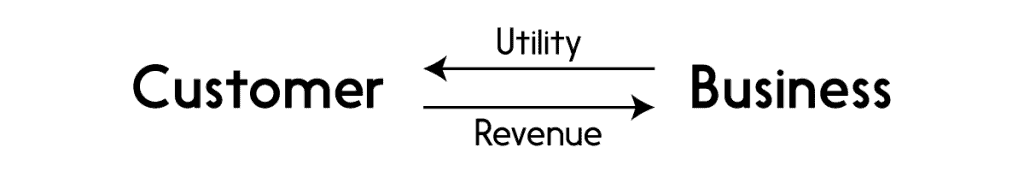
- Asymmetric Revenue Model
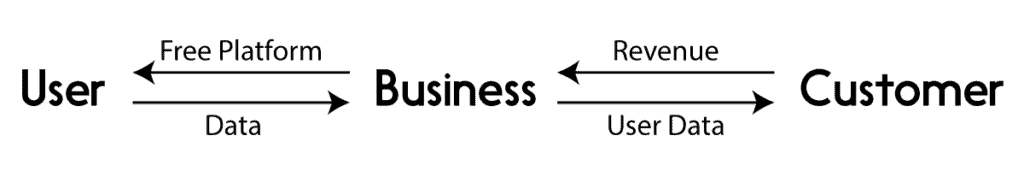
How to choose between one of the 16 revenue models?
- Research how the customer wants to buy from you
Is your product in the store or do you maybe sell through a web shop?
- Check what the average frequency is with which a customer buys
It may be that the customer prefers to just have an amount debited periodically to make unlimited use of something or that person prefers to pay for a one-time transaction.
- See what revenue model your competitors apply
Do your competitors sell ad space or do they maybe charge per user?
- Explore how to make the value of the price as close as possible to the value the customer receives
When does the customer achieve the end result? Can you align price with the customer’s end result? Perhaps the North Star Metric can be helpful here.
You will have to experiment yourself to see which revenue models work for your business and product, but perhaps the image below will help you:
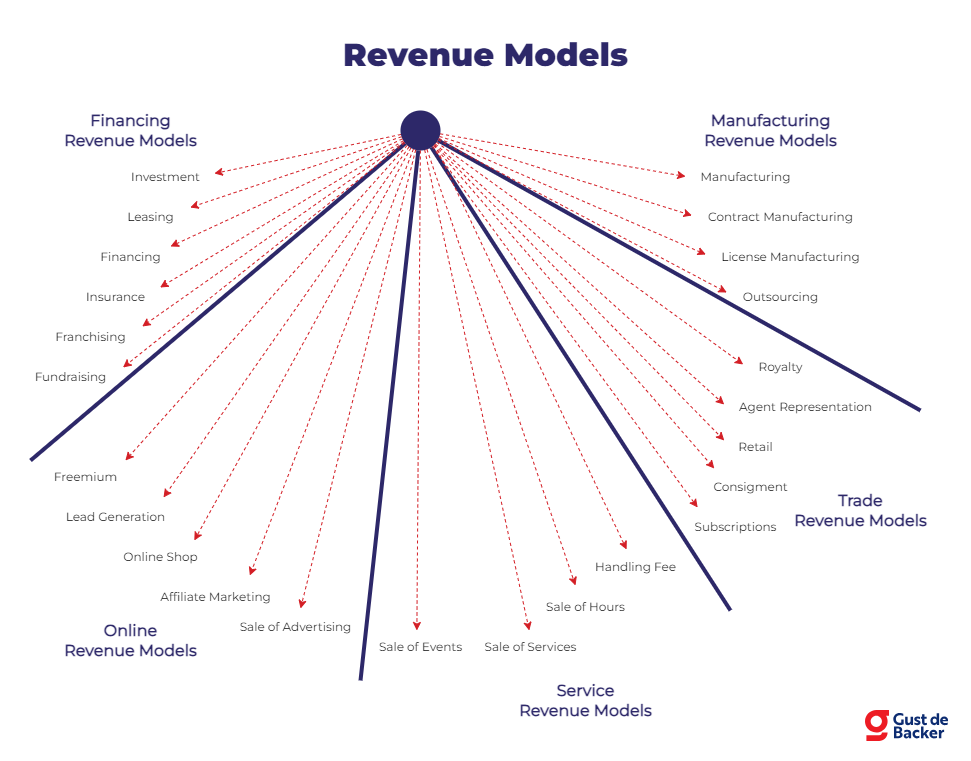
Then we’ll wrap up now…
How are you going to make money?
So, now you know what revenue models are out there…
I want to know from you, which revenue model do you apply and why?
Let me know in a comment below.
P.S. if you would like additional help please let me know at [email protected]
Frequently asked questions
A revenue model is a company’s strategy for making money from the value it delivers to customers.
There are many different revenue models, but there are at most 15 that are very commonly applied. Examples are the advertising model, brokerage model, transaction model, licensing model or the rental model.
Online, there are many revenue models that can be applied, but often you will see the transaction model, subscription model, freemium model, consumption model or the advertising model recurring.
The revenue model is about the strategy the company chooses to make money from the value it delivers to the customer and the pricing strategy reflects how the price of the revenue model is determined.

![BCG Matrix (2026): Meaning and Example [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/BCG-Matrix.png)
![Lean Canvas (2026): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Lean-Canvas.png)


Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.