Market research is important for any business….
Most companies fail because they develop something the market doesn’t want or because they don’t move with the market fast enough.
I’m going to show you:
- What market research is
- What components are involved in market research
- How to do market research
Let’s start quickly…
What is market research?
Market research consists of surveys and analyses that identify your market, or competition, customers and positioning.
It is easy to outsource market research, but it is also easy to do yourself. In fact, market research gives you the most important insights you need to set up or grow your business.
Why is market research important?
The book The Lean Startup states that the number one reason start-ups fail is because they bring a product to market that no one is waiting for:

Market research allows you to understand what the market wants and where the market is moving. A problem-solution fit or product-market fit helps measure your progression of this.
Marketing myopia
The goal is not to sell your products but to provide the customer with his needs. Customers never need a product or service, they only want the solution.
The goal isn’t to sell things, it’s to satisfy customer needs. – Theodore Levitt
12 components of market research
In doing market research, I always distinguish between the qualitative and quantitative research:
1. Quantitative research
Quantitative research focuses on data that is expressed in numbers, tables, graphs and/or charts. It’s particularly used for gathering facts of issues and matters about which quite a bit is already known.
1.1 Desk research
The term actually gives it away a bit, desk research is the research you do at your desk.
Collecting information based on existing research (also called secondary research) is desk research.
The benefits of this are:
- It can save time.
- The costs are lower.
- A lot of data is available.
The disadvantages are:
- Information does not connect seamlessly to the objective.
- Existing data may be outdated.
- There may be subjective perception.
1.2 Market segmentation and size
Market segmentation is generally done on 5 different components:
- Demographic criteria: components such as age, life stage, gender, ethnicity, culture, etc.
- Geographic criteria: consider country, region, city, size of city, climate, etc.
- Socio-economic criteria: income, occupation, education, etc.
- Psychographic criteria: personal characteristics, lifestyle, etc.
- Behavioral criteria: loyalty, degree of use, buying frequency, digital intelligence, usage, etc.
Dividing the market into certain segments helps you to:
- Align business strategy with different types of buyers.
- Customer-centric marketing strategy.
- Proper positioning for each type of buyer.
To effectively and efficiently determine your go-to-market strategy and the size of your market, it is helpful to use the TAM SAM SOM model:
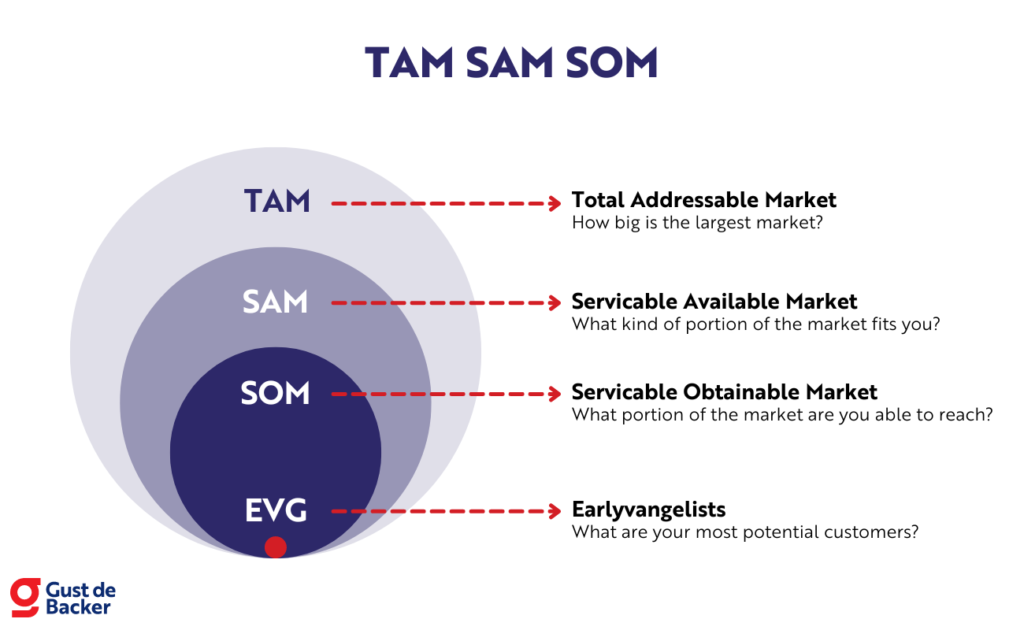
This model allows you to divide the market into 4 segments so that you can focus your resources on the most potential market, but still have a good picture of the total size of the market.
Also, the TAM SAM SOM model allows you to bridge the ‘Chasm’ between the Early Adopters and the Early Majority:
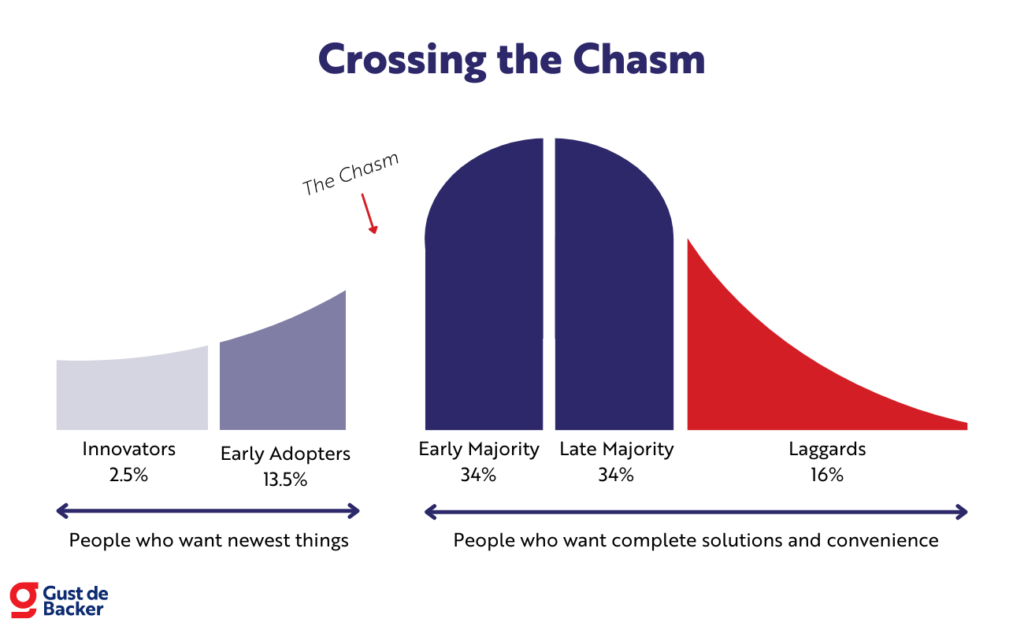
Indeed, the Early Adopters are content with a solution that is not quite perfect yet while the Early Majority wants a simple, easy and effective solution.
1.3 Search volume
Also a well-known way to determine how much demand there is from the market is a keyword survey:

By looking at search volumes and competition, it is possible to estimate how much demand there is for a particular product or service and how much competition there is to meet that demand. Using a tool like SEMrush or Ubersuggest, you can do this easily.
1.4 Trends and developments
What is easier to start a business than to respond to current trends and developments …
By setting up your business around a trend or development, it is possible to jump on a gap in the market where there is a lot of demand, but where there is still (relatively) little supply.
Think for example of the trend of online shopping, by setting up a webshop early for products that are standard and of which it is difficult and expensive to place them all in a store (books 😉 ) you can respond perfectly to a changing landscape.
The DESTEP analysis allows you to identify trends and developments, which will be covered later in this article.
1.5 Competition
Most markets have some form of competition. Even the blue ocean market often has competition, as Spotify entered a blue ocean market, but still competed with CDs.
With competition, you can look at several things:
- Average revenue
- Positioning
- Price/quality
- The product range
- The service and support
- Distinctive character
- Target group
- Marketing
- Location
- Strengths/Weaknesses
- Costs to switch
New Lanchester Strategy
A market can be divided using the New Lanchester Strategy:
- One company has more than 74% of the market share, you then speak of a monopoly. This type of market is extremely difficult to approach.
- The combined market share of the market leader and the second largest company is more than 74% and the market leader is 1.7 times larger than the number two. This is referred to as a duopoly. This market is also very difficult to approach.
- A company with 41% market share that is at least 1.7 times as big as the number two can be labeled as a market leader. In this type of market it often works well to introduce a new segment.
- If one company has no more than 26% market share, anything is still possible.
- If the largest market share of one company within the market is less than 26% then there is no real market leader, this market is relatively easy to approach.
1.6 Starters and stoppers
Look at how many people start and stop each year within your industry, this indicates how healthy your industry is. If many companies go bankrupt, it is a risk, but also an opportunity if you can create a more efficient business model.
You can find this information online at the Chamber of Commerce.
1.7 Surveys with closed questions
Closed-ended surveys are also part of quantitative research, but ideally are used only when validating a particular assumption or analyzing a benchmark or result.
2. Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on words and meanings to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research is particularly useful in gaining insight into topics about which there is still little knowledge.
2.1 In-depth interviews
An in-depth interview can be used for:
- Discovering a problem in the market
- Discover solutions to a problem
- Validate problem in the market
- Validate solution to the problem
- Mapping the Decision-Making Unit.
Some rules in conducting customer interviews:
A few more learnings I can share from experience:
- Introduce yourself as someone who is doing research, not someone who is trying to sell a product. It is important not to use the word ‘research’, but to start with ‘Can you help me?’ or ‘I spoke to … who referred me to you’.
- Compliments about the solution is a form of noise, you are not looking for compliments but for concrete and hard validation such as a signature or visible motivation towards the product or service.
- Any feedback you get about future situations is not useful, ‘I don’t have a problem now, but maybe in the future’, ‘If you add A, B and C then I do want to work with you’.
- Don’t generalize, you want to know specifically what the problem is, how big that problem is, what the consequences of that problem are and who is involved in the problem. The same applies to the solution.
- Hearing someone say something once is not validation, you want to have as many conversations as possible to be as sure as possible of your findings.
- If you can’t find a specific niche with a specific problem then it is impossible to create a solution for it.
Possibly you could use the STAR / LSD method for this or immerse yourself in Customer Development.
Customer problem statement
Finally, you can then complete a customer problem statement:
“Our [target audience] is experiencing problems with [customer experience]. Based on [considerations], they are now solving this with [alternative solution]. The disadvantages of this are [complaints].”
2.2 Surveys with open questions
Surveys with open questions are also a form of market research. For example, consider a converters survey, or a survey that you put on the thank you page of your web shop or form to ask some open questions.
Hotjar even offers a Product-Market Fit survey to validate your Product-Market Fit.
Optionally, you could also send respondents a questionnaire with open questions, but then I would personally prefer an in-depth interview, because then you can ask more questions.
2.3 Target group research
Concrete insight into the different segments of your target audience based on:
- What they find important
- What kind of people they are
- How much they have to spend
- What the ages are
It’s also possible to do review mining of your competitors or yourself to get some voice of customer data.
2.4 Expert interview
Interviews do not have to be with (potential) customers only, but can also be with experts within a branch or industry. Ask for example about their experience, what they notice, what they see and if they can confirm or refute your assumptions.
2.5 Observations
Sometimes people don’t say what they do and don’t do what they say….
The solution to this is to observe them and see what the behavior is and perhaps whether the behavior changes with a particular solution.
Observe, take notes and perhaps ask if anyone can explain their behavior.
Market research example
Suppose you want to start a construction market (chain), you can start by dividing the market into different segments/personas. For example:
- Non-handy young adults
- Handyman father
- Independent worker
Questions you can answer with market research in doing so:
- What are the characteristical traits of this persona?
- What is important to this persona?
- How does this persona make a purchase?
- What does the customer journey look like?
- What are the important aspirations of this persona?
- How big is the market?
- What are the demographics of this persona?
- Where does this persona live?
- What type of home does this persona have?
- What does this persona have to spend?
- How does this persona go about seeking information?
- What does this persona perform themselves and what does this persona outsource and why?
- What is the frequency that this persona interacts with you?
- Whose opinion does this persona consider important?
- What media can this persona be reached with?
- What does this persona consider important in making a choice?
- Why does this persona choose a particular brand or solution?
- How might this persona be influenced?
- What solutions or competitors does this persona consider?
- How much is the persona willing to spend on a solution?
- What problem does this persona have?
- What solutions does this persona use for their problems?
Well-known marketing models
There are also some well-known marketing models that you can use to conduct market research, such as:
- Porter’s 5 forces model: determine competition in the market based on:
- Potential entrants
- Strength of substitutes
- Supplier strength
- Buyer power
- Competitive power of players in the market among themselves
- DESTEP Analysis: find opportunities and threats in the market using:
- Demographic factors
- Economic factors
- Socio-cultural factors
- Technological factors
- Ecological factors
- Political-legal factors
- Context Map: is very similar to the DESTEP Analysis, but slightly more comprehensive.
- Ansoff Matrix: can be used to determine the growth strategy of a company. There are 4 different growth strategies you can apply from the Ansoff Matrix:
- Market Development
- Market penetration
- Diversification
- Product development
- Value Strategies of Treacy and Wiersema: a company should be good at 3 of the value strategies and excellent at one of the value strategies.
- SWOT Analysis: identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- BCG Matrix: find out which product groups are interesting to keep or which product groups are better to let go. The product groups are divided into:
- Dogs
- Question marks
- Cash cows
- Stars
- TAM SAM SOM: Map out your go-to-market strategy by dividing the market into manageable chunks. TAM SAM and SOM are acronyms for:
- Total Addressable Market
- Serviceable Available Market
- Serviceable Obtainable Market
Red or Blue Ocean
There is a difference between a Red or Blue Ocean market:
| Red Ocean (bestaande markt) | Blue Ocean (nieuwe markt) |
| Compete in an existing market | Create a market without competition |
| Wanting to beat the competition | Making the competition irrelevant |
| Leverage existing market demand | Create and capture market demand |
| More value versus higher cost or less value versus lower cost | There is no reference material to compare value or cost with |
Based on this, you can more easily choose how to approach the market:
- Existing market (Red Ocean)
- New market (Blue Ocean)
- New segment in an existing market
- Niche strategy
- Cost-leader
Start Investigating…
Now it’s your turn, Get Out Of The Building and start researching.
I’m curious, what do you think is the most efficient form of market research?
Let me know in a comment.
P.
P.S. could you use some extra help? Send an e-mail to [email protected]
Frequently asked questions about Market Research
Market research consists of surveys and analysis that identify your market, or competition, customers and positioning. There are many different types of research, but desk research combined with customer interviews and questionnaires are often used.
Good market research consists of different customer segments/personas, in-depth understanding of the competition, estimation of the market size, and content understanding of different customer segments.
Exploratory: exploratory research into a problem statement. Descriptive: descriptive research into a problem statement. Explanatory: research into relationships between variables. The requirements of a market research study are a report of the findings, a good questionnaire and the representativeness of the study.
Market research aims to explore the market, to know what is going on, who is in the market, who are your customers, what your customers care about, etc.

![Business-Driven Marketing (BDM): 8 Steps to Drive Business Impact [+14 Templates]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Business-Driven-Marketing-BDM.png)
![Automate ~30% of Repetitive Marketing Tasks with AI: 5 Easy Steps [+ 7 Expert Prompts]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/AI-in-Marketing.png)
![Customer Journey Map (2025): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Customer-Journey-Map.png)
I have been checking out many of your stories and i can state pretty clever stuff. I will make sure to bookmark your site.
Great to hear! If you have any more questions, feel free to ask them.
Gust du Backer, this was a fascinating read! Market research is all about acquiring market insights and marketing aspects. It addresses all elements influencing both, such as consumer and sales analysis, among others. Whether we are analyzing data for the red or blue oceans, I feel that market research is crucial, and the key aim is to listen to customers’ opinions, rely on credible sources, and understand the stages of what you do to ensure the market strategy’s success.
Thank you, Philip!
Great piece article with complete step-by-step clear ideas about market research techniques. All businesses should undergo a market research analysis before entering into the real world. It helps in knowing their competitor better and gaining crystal clear ideas about their target audience.
Thank you, Dhananjay!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for the good writeup. It actually was a amusement account it.
Glance advanced to more added agreeable from you! However,
how can we keep in touch?